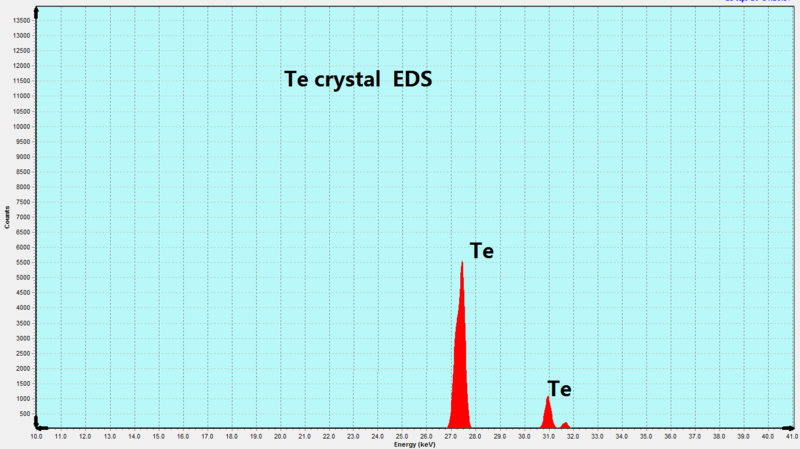
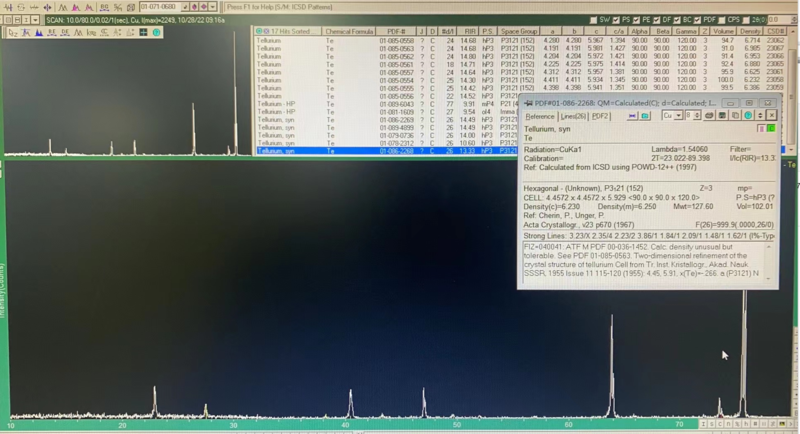
Description
Te Crystals (Tellurium)
Tellurium (Te) is a semimetallic element with a trigonal crystal structure, widely used in electronic, optoelectronic, and thermoelectric applications. Its unique anisotropic properties, combined with excellent thermal and electrical conductivity, make it an essential material for advanced research and industrial applications.
Sample Size Options:
Crystals larger than 10 mm²
Material Properties:
Crystal Structure: Trigonal layered structure with a helical atomic arrangement.
High Anisotropy: Strong direction-dependent electrical and thermal properties.
Semimetallic Conductivity: Exhibits a narrow bandgap (~0.35 eV).
Thermoelectric Properties: High Seebeck coefficient and low thermal conductivity, ideal for energy conversion.
Crystal Structure:
Type: Trigonal (P3₁21 space group).
Features: Easily cleavable along certain crystallographic planes for advanced studies.
Degree of Exfoliation:
Ease of Use: Can be exfoliated into thin layers for 2D material research and device fabrication.
Other Characteristics:
Thermoelectric Performance: Highly suitable for thermoelectric applications due to its low thermal conductivity and strong Seebeck effect.
Optical Properties: Absorbs strongly in the infrared region, suitable for photonic applications.
Environmental Stability: Stable under controlled storage conditions, with moderate sensitivity to oxidation.
Applications:
Thermoelectric Devices:
Ideal for waste heat recovery and energy harvesting systems.
Optoelectronics:
Suitable for infrared detectors, lasers, and photonic devices.
2D Material Research:
Perfect for exfoliation into thin layers for exploring anisotropic properties.
Energy Storage:
Promising for use in batteries and energy storage devices.
Quantum Materials Research:
Enables studies of semimetallic and low-dimensional electronic behavior.
Additional information
| CAS Number | 13494-80-9 |
|---|